10 Amazing Things You Didn’t Know About Lake Victoria
Lake Victoria, Africa’s largest freshwater lake, is a natural wonder straddling Uganda, Kenya, and Tanzania. Known as Lake Victoria Africa, this vast water body is the second-largest freshwater lake globally, renowned for its stunning biodiversity, vibrant ecosystems, and economic significance.
Named after Queen Victoria, the lake supports millions of livelihoods through fishing, transport, and tourism. Its shimmering waters host diverse wildlife, unique islands, and rich cultural heritage tied to local tribes. However, environmental challenges like pollution and overfishing threaten its sustainability.
Where is Lake Victoria Located?
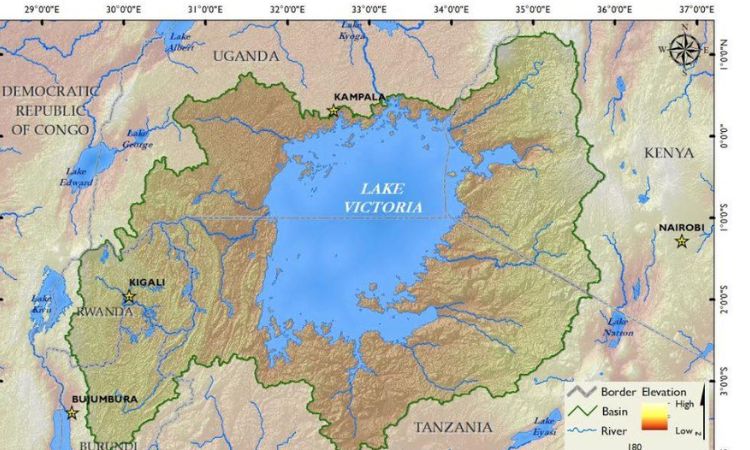
Lake Victoria lies in East Africa, shared by three countries: Uganda, Kenya, and Tanzania. Positioned at the heart of the African Great Lakes region, it sits at coordinates approximately 0°S to 3°S latitude and 31°E to 34°E longitude.
The lake is bordered by Uganda to the north, Kenya to the northeast, and Tanzania to the south and west. Its strategic location makes it a central hub for regional trade and cultural exchange.
Major cities like Kampala in Uganda, Kisumu in Kenya, and Mwanza in Tanzania thrive along its shores, benefiting from its resources and connectivity. Lake Victoria’s accessibility enhances its appeal for Lake Victoria tourism and cross-border activities.
Geography and Size of Lake Victoria
Lake Victoria is a geographical marvel, covering an area of approximately 68,800 square kilometers (26,560 square miles), making it Africa’s largest lake and the second-largest freshwater lake globally, after Lake Superior.
Its maximum length is about 337 kilometers, and its width reaches 240 kilometers. The lake’s depth averages 40 meters, with a maximum depth of 84 meters.
Its shoreline stretches over 7,142 kilometers, dotted with bays, inlets, and wetlands. Fed by numerous rivers, including the Kagera River, and drained by the Nile River, Lake Victoria’s size and depth make it a critical freshwater reservoir, supporting Lake Victoria fishing and regional ecosystems.
How Deep is Lake Victoria
Lake Victoria has an average depth of about 40 meters (131 feet) and a maximum depth of approximately 84 meters (276 feet). Its relatively shallow depth, compared to other African Great Lakes, results from its formation in a tectonic depression. This Lake Victoria size and depth supports diverse ecosystems, Lake Victoria fishing, and tourism, but also makes it vulnerable to environmental challenges like pollution and sedimentation.
History and Formation of Lake Victoria
The history of Lake Victoria dates back approximately 400,000 years, formed through tectonic activity in the East African Rift System.
Unlike other African Great Lakes, Lake Victoria is relatively young and shallow, resulting from the uplifting of surrounding landmasses that created a depression filled by rainfall and rivers.
Named in 1858 by British explorer John Hanning Speke after Queen Victoria, the lake has been a focal point for exploration and trade. Indigenous communities, such as the Luo and Baganda, have lived along its shores for centuries, shaping its cultural legacy.
Its history reflects both natural evolution and human interaction, influencing its modern significance.
What is Lake Victoria Famous For?
Lake Victoria is renowned for several reasons. It is the source of the Nile River, one of the world’s longest rivers, making it a geographical landmark.
Its vast size and biodiversity, particularly its fish species like Nile perch and tilapia, make it a hub for Lake Victoria fishing. The lake’s scenic islands, such as Ssese and Rubondo, draw tourists for their natural beauty and wildlife.
Additionally, its role in supporting millions of livelihoods through fishing, transport, and hydroelectric power cements its economic importance.
it’s cultural significance, tied to local tribes and their traditions, further enhances its fame as a vibrant, multifaceted destination in Lake Victoria Africa.

Lake Victoria Animals
The lake’s diverse ecosystem supports a rich array of animals, making it a biodiversity hotspot in East Africa. The lake is home to over 200 fish species, notably the Nile perch and tilapia, which dominate Lake Victoria fishing, though the invasive Nile perch has reduced native cichlid populations.
Aquatic life includes Nile crocodiles, hippos, and otters, which thrive in its waters and along its shores. The surrounding wetlands and islands, like Ssese and Rubondo, host mammals such as sitatunga antelopes, elephants, and chimpanzees, particularly in Rubondo Island National Park.
Birdlife is vibrant, with African fish eagles, kingfishers, herons, and cormorants attracting birdwatchers for Lake Victoria birding, while conservation efforts aim to protect this delicate wildlife balance.
Importance of Lake Victoria to Local Communities
Lake Victoria is a lifeline for millions of people in Uganda, Kenya, and Tanzania. It supports livelihoods through fishing, which employs over 2 million people and provides protein for local diets.
The lake facilitates transport, connecting communities via ferries and boats, and supports agriculture through irrigation. Hydroelectric power from the Nile’s outflow powers regional economies.
For local tribes like the Luo, Baganda, and Sukuma, the lake holds cultural and spiritual significance, woven into traditions and folklore.
Its economic and social importance underscores its role as a vital resource, driving calls for sustainable management to ensure its benefits endure.
Major Islands on Lake Victoria
This vast lake is dotted with picturesque islands, each offering unique attractions. The Ssese Islands in Uganda, an archipelago of 84 islands, are known for pristine beaches, hiking, and cultural experiences.
Ukerewe Island in Tanzania, the largest island on the lake, is a hub for fishing and agriculture, with vibrant markets and historical sites. Rubondo Island in Tanzania, a national park, is a haven for wildlife, including elephants, giraffes, and chimpanzees, ideal for eco-tourism.
These Lake Victoria islands attract visitors for their natural beauty and biodiversity, offering opportunities for Lake Victoria tours, birding, and relaxation amidst stunning landscapes.

Best Islands on Lake Victoria to Visit
For travelers, the best islands to visit include:
- Ssese Islands (Uganda): Ideal for beach relaxation, hiking, and cultural tours, with resorts like Brovad Sands Lodge.
- Rubondo Island (Tanzania): A national park perfect for wildlife enthusiasts, offering safaris to spot chimpanzees and elephants.
- Ukerewe Island (Tanzania): Great for cultural immersion, with bustling markets and historical sites.
- Mfangano Island (Kenya): Known for ancient rock art and serene fishing villages.
These islands offer diverse Lake Victoria activities, from adventure to tranquility, making them top picks for Lake Victoria tourism.
Tourism Activities on Lake Victoria
Lake Victoria tourism is thriving, offering diverse activities for adventurers and nature lovers. Lake Victoria boat rides provide scenic tours, allowing visitors to explore islands and spot wildlife.
Fishing trips are popular, with anglers targeting Nile perch and tilapia. Birding attracts enthusiasts to observe species like the African fish eagle and cormorants.
Cultural tours immerse visitors in local traditions, while hiking and cycling on islands like Ssese offer adventure. Water sports, such as kayaking, and beach relaxation are also highlights.
Key attractions include Jinja in Uganda for Nile River adventures, Kisumu in Kenya for cultural festivals, and Mwanza in Tanzania for rock formations and history.
Whether you’re drawn to Lake Victoria Uganda, Kenya, or Tanzania, this iconic lake promises unforgettable experiences and a deeper appreciation for Africa’s natural and cultural treasures. Plan your visit to discover the magic of Lake Victoria Africa.
Can You Swim in Lake Victoria?
Swimming in Lake Victoria is possible but requires caution. The lake’s waters are generally warm, but risks like bilharzia (a parasitic disease), crocodiles, and hippos make swimming unsafe in some areas.
Pollution, particularly near urban centers, can also affect water quality. Safe swimming spots include designated areas near resorts on the Ssese Islands or private beaches in Jinja, where water is clearer and monitored.
Visitors should consult local guides, avoid murky waters, and check for health advisories before swimming. For a safer experience, opt for Lake Victoria boat rides or other water-based activities to enjoy the lake’s beauty.
Best Time to Visit Lake Victoria
The best time to visit depends on weather and activities. The dry seasons—June to August and December to February—offer pleasant weather for Lake Victoria boat rides, birding, and island exploration.
Temperatures range from 20°C to 28°C, with clear skies ideal for outdoor activities. The wet seasons, March to May and September to November, bring lush greenery, perfect for photography and birdwatching, though rain may disrupt travel.
For fishing, the dry seasons are optimal due to calmer waters. Planning around local festivals, like Kisumu’s cultural events, enhances the experience. Always check weather forecasts for specific Lake Victoria attractions.
Lake Victoria in Uganda, Kenya, and Tanzania – Key Attractions
Each country offers unique Lake Victoria attractions. In Uganda, Jinja is a gateway to the Nile’s source, offering white-water rafting, kayaking, and visits to the Ssese Islands.
Kenya’s Kisumu features Dunga Beach for fishing and birding, plus cultural experiences at the Kisumu Museum. In Tanzania, Mwanza’s Bismarck Rock and Rubondo Island National Park attract nature lovers and adventurers.
Lake Victoria Uganda, Kenya, and Tanzania each provide distinct experiences, from adrenaline-pumping activities to serene island getaways, making the lake a versatile destination for Lake Victoria tours tailored to diverse interests.
Economic Importance of Lake Victoria
Lake Vic lake drives economic activity across the region. Fishing is a cornerstone, with the Nile perch and tilapia industries generating millions in revenue and supporting export markets.
The lake serves as a vital transport route, with ferries connecting Uganda, Kenya, and Tanzania, facilitating trade. Hydroelectric power from the Nalubaale Dam in Uganda harnesses the Nile’s flow, supplying electricity to millions. Agriculture benefits from irrigation, boosting crop production.
Tourism, including Lake Victoria boat rides and island tours, contributes significantly to local economies. The lake’s multifaceted economic role underscores its importance, though sustainable practices are critical to maintaining these benefits.
Environmental Challenges Facing Lake Victoria
This lake faces significant environmental challenges. Pollution from industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and untreated sewage threatens water quality and aquatic life.
Invasive species, particularly the Nile perch, have decimated native fish populations, disrupting ecosystems. Overfishing depletes stocks, endangering livelihoods dependent on Lake Victoria fishing.
Deforestation and wetland degradation exacerbate erosion and habitat loss. Climate change impacts water levels and weather patterns, affecting agriculture and transport.
Conservation initiatives, such as water quality monitoring and invasive species management, are underway, but coordinated efforts among Uganda, Kenya, and Tanzania are essential to address these challenges and ensure Lake Victoria’s sustainability.
Lake Victoria Map
Cultural Significance and Local Tribes around Lake Victoria
This lake is deeply intertwined with the cultural heritage of the surrounding tribes. The Luo in Kenya, known for fishing expertise, revere the lake as a source of life.
The Baganda in Uganda incorporate the lake into spiritual practices, with historical sites like the Kasubi Tombs reflecting its influence.
The Sukuma in Tanzania share folklore tied to the lake’s islands. Annual festivals, such as the Luo’s boat racing events, celebrate the lake’s role in community identity.
These tribes’ traditions enrich Lake Victoria tourism, offering visitors cultural immersion through music, dance, and storytelling, preserving the lake’s cultural legacy.
Hotels and Accommodation Near Lake Victoria
Accommodation near Lake Victoria caters to diverse budgets and preferences. In Uganda, Jinja offers options like the Nile Resort Jinja (luxury) and budget-friendly guesthouses on the Ssese Islands.
Kenya’s Kisumu features hotels like Acacia Premier Hotel and affordable lodges near Dunga Beach. In Tanzania, Mwanza’s Malaika Beach Resort provides upscale stays, while budget campsites are available near Rubondo Island.
Many accommodations offer lake views, access to Lake Victoria boat rides, and proximity to attractions, ensuring memorable stays.
Booking in advance, especially during peak seasons, is recommended for the best Lake Victoria tourism experiences.
Interesting Facts About Lake Victoria
Here are some compelling Lake Victoria facts:
- It’s the source of the Nile River, one of the world’s longest rivers.
- The lake supports over 30 million people across three countries.
- It was named by John Hanning Speke in 1858 after Queen Victoria.
- Lake Victoria’s cichlid fish species are a focus of evolutionary biology studies.
- The lake’s surface area is larger than some countries, like Switzerland.
- It experiences unique “lake effect” weather, creating sudden storms.
- The Ssese Islands are a biodiversity hotspot, hosting rare primates.
These facts highlight why Lake Victoria Africa remains a fascinating destination for researchers and tourists alike.
Future of Lake Victoria Conservation and Sustainability
The future of Lake Victoria hinges on robust conservation efforts. Initiatives like the Lake Victoria Basin Commission promote sustainable management, focusing on reducing pollution, controlling invasive species, and regulating fishing.
Reforestation and wetland restoration projects aim to combat erosion and habitat loss. Community-led programs educate locals on sustainable practices, balancing economic needs with environmental protection.
International partnerships fund water quality monitoring and renewable energy projects to reduce reliance on the lake’s resources.
For Lake Victoria to thrive, coordinated policies among Uganda, Kenya, and Tanzania are crucial, ensuring this vital ecosystem supports future generations while preserving its biodiversity and cultural heritage.
